DAS
Cellular Boosting Solutions
Say goodbye to poor cell phone reception and hello to seamless communication with QCTV’s Commercial Cellular Boosting Solutions.
What is DAS?
In-building Distributed Antenna Systems (DAS) are used to improve wireless coverage and capacity inside buildings, such as commercial office buildings, hospitals, airports, and sports venues. A DAS is a network of antennas, cabling, and signal amplifiers that distribute cellular and wireless signals throughout the building, providing improved coverage and connectivity for end-users.
DAS systems can support multiple wireless frequencies and technologies, such as 3G, 4G, and 5G cellular networks, Wi-Fi, and public safety communications. They can be designed for both indoor and outdoor use, and can be customized to meet the specific needs of a building or facility.
Designing and implementing an effective DAS solution requires a deep understanding of wireless communications technology, building materials, and the unique needs of each client. It typically involves site surveys, analysis of wireless traffic patterns, and careful planning to ensure optimal performance and coverage.
Commercial Cellular Boosting Solutions Keep Your Property Safe and Up-To-Code
As a property owner or manager, ensuring the safety of your occupants is a top priority. That’s why cities and municipalities require that first responders have the ability to communicate throughout a building in an emergency situation. At QCTV, we understand the importance of being prepared for the unexpected, and we are here to help. Our team of experts has extensive experience in designing and installing in-building public safety communication systems that meet the highest standards.
Our goal is to help you get back up to code, and we will work with the local public safety agencies to ensure that your building is compliant with all applicable local codes. Our team of experts has a wealth of knowledge and experience in the industry, and we use this to our advantage to recommend the best solution for your specific needs. Whether it’s a simple analog system or a complex digital system, we will ensure that your building is equipped with the best technology available.
In today’s fast-paced world, a reliable and strong cell phone signal is crucial for businesses to maintain professional and efficient communication with customers, employees, and partners. Unfortunately, poor cell phone reception can cause dropped calls, slow data, and ultimately leave a negative impression on your business.
That’s where QCTV comes in. Our team of experts is dedicated to providing you with the best indoor cellular coverage solutions to eliminate poor cell phone signals and keep you connected. Our process consists of five simple steps:
- Analysis: Our team will assess your current cellular coverage and identify areas in need of improvement.
- Design and Installation: Based on our analysis, we will design a custom solution tailored to your unique needs and install the equipment to ensure optimal performance.
- Local Government & Safety Regulations: We will work with local public safety agencies to ensure that your building is compliant with all applicable local codes.
- Commissioning, Testing & Integration: Our team will test and commission the system to make sure it’s working smoothly and seamlessly integrate it into your existing infrastructure.
- Maintenance, Troubleshooting, and Upgrades: Our team is always available to provide ongoing support, troubleshoot any issues, and upgrade your system as needed to keep you connected.
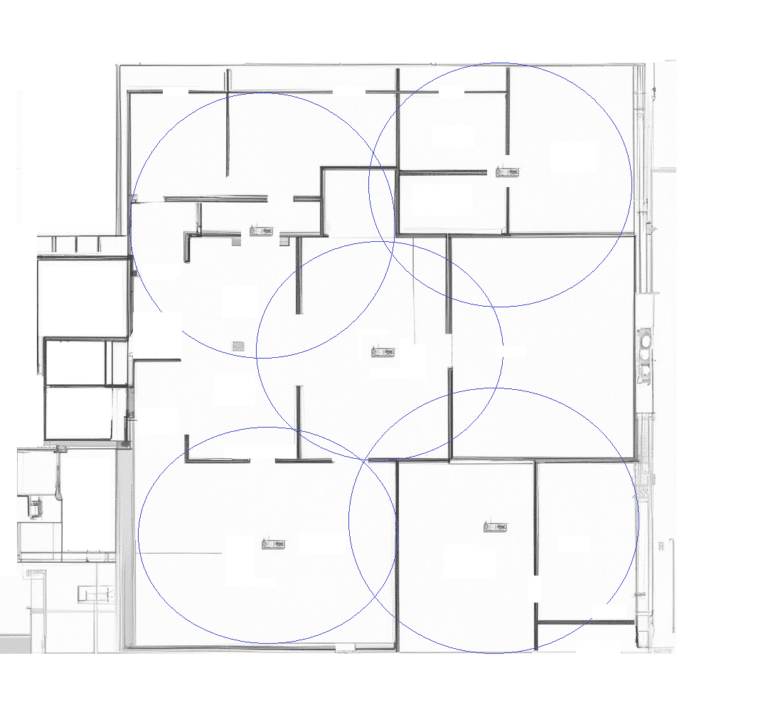
A Distributed Antenna System (DAS) site survey
A Distributed Antenna System (DAS) site survey is an important step in the design and implementation of a DAS in a building or other structure. The purpose of a site survey is to assess the site for factors that may affect the performance of the DAS, such as signal strength, interference, and building materials.
During a DAS site survey, a technician will typically perform the following tasks:
- Signal measurements: The technician will use specialized equipment to measure the strength of existing cellular signals within the building.
- Building analysis: The technician will assess the building’s layout, construction materials, and any other factors that may affect signal propagation.
- Antenna placement: The technician will identify the best locations for DAS antennas to ensure optimal signal coverage.
- Cable routing: The technician will plan the routing of cables to ensure that signal loss is minimized and interference is avoided.
- Interference analysis: The technician will identify potential sources of interference, such as other wireless devices or electrical equipment, and take steps to mitigate their effects on the DAS.
The information gathered during a site survey is used to create a detailed design plan for the DAS, which includes the type and placement of antennas, the routing of cables, and other specifications needed for installation. By conducting a thorough site survey, a DAS installer can ensure that the system is optimized for the specific needs of the building and its occupants.
Frequently Asked Questions
A DAS (Distributed Antenna System) is a network of antennas that are strategically placed throughout a property to enhance cellular coverage and provide better wireless connectivity. The system works by collecting and redistributing cellular signals from nearby cell towers to improve the quality of wireless coverage throughout the property.
A DAS system can provide several benefits to your property, including improved wireless coverage, increased tenant satisfaction, higher property value, and the ability to attract new tenants. With a reliable and efficient DAS system in place, your property can offer seamless connectivity and a better overall experience for your tenants.
The costs of deploying a DAS system can vary depending on the size of the property, the number of antennas required, and the level of customization needed. QCTV can provide a customized quote based on the specific needs of your property.
There are few risks or drawbacks associated with deploying a DAS system, as long as the system is installed properly and maintained well. QCTV will work closely with you to ensure that the DAS system is designed and installed to meet your specific needs and to minimize any potential risks or drawbacks.
The installation requirements for a DAS system can vary depending on the size of the property and the number of antennas required. However, QCTV’s installation process is designed to be minimally disruptive to your property’s operations. We work efficiently and effectively to ensure that the installation process is completed quickly and with minimal disruption to your property.
The length of time it takes to install a DAS system can vary depending on the size of the property and the number of antennas required. However, with QCTV’s experience and expertise, we can complete most installations within a reasonable timeframe and with minimal disruption to your property.
A DAS system typically requires minimal maintenance or upkeep. However, regular monitoring and inspections are recommended to ensure that the system is functioning properly. QCTV can provide ongoing maintenance and support to ensure that your DAS system is operating at optimal performance.
If the DAS system requires repairs or upgrades, QCTV can provide the necessary services and support. Our team of experts will work closely with you to determine the best course of action and provide a timely and effective solution.
QCTV provides training and education to ensure that your staff is properly equipped to use and manage the DAS system. Our training sessions are designed to be informative and easy to understand, and we are always available to provide ongoing support and assistance as needed.
More information
The regulation of Distributed Antenna Systems (DAS) has evolved over the years as the technology has become more prevalent in buildings and public spaces. Here’s a brief history of some of the major regulations affecting DAS:
- 1996 Telecommunications Act: This law allowed for the expansion of wireless services and set up the framework for the regulation of the wireless industry. It included provisions for the deployment of antennas and other wireless infrastructure.
- FCC’s DAS Rules: In 2002, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) established rules for DAS to ensure that wireless providers had access to the necessary infrastructure to provide services to their customers. These rules established standards for DAS and required building owners to allow wireless providers access to their buildings to install DAS.
- Middle-Class Tax Relief and Job Creation Act of 2012: This law included provisions for the deployment of DAS in federal buildings and public safety facilities.
- FCC’s Small Cell Order: In 2018, the FCC issued an order to streamline the deployment of small cell infrastructure, including DAS. This order made it easier for wireless providers to install DAS in public rights-of-way and on other publicly-owned properties.
Overall, regulations affecting DAS have been aimed at ensuring that wireless providers have access to the infrastructure they need to provide services to their customers, while also balancing the interests of building owners and the public.
The regulations affecting Distributed Antenna Systems (DAS) compliance have evolved over the years as the technology has advanced and become more widely used. Here is a brief history of some key regulations:
- In 2013, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) issued a declaratory ruling and order that clarified the regulatory treatment of DAS under the Communications Act. The ruling confirmed that DAS is subject to the same regulatory requirements as traditional wireless providers, including the requirement to obtain an FCC license for operating wireless infrastructure.
- In 2014, the FCC issued a further ruling that streamlined the process for obtaining licenses for DAS, making it easier for companies to deploy DAS networks.
- In 2016, the FCC issued rules that established new regulatory requirements for DAS and other small cell wireless infrastructure. These rules aimed to facilitate the deployment of small cell infrastructure to support 5G networks, while also addressing concerns around local control and environmental impacts.
- In 2018, the FCC issued an order that further streamlined the process for deploying DAS networks and other small cell infrastructure, particularly on government-owned property. This order aimed to speed up the deployment of 5G networks and improve coverage in urban areas.
Overall, the regulations affecting DAS compliance have generally aimed to balance the need for wireless infrastructure with the concerns of local communities and government agencies. As DAS and other wireless technologies continue to evolve, it is likely that further regulatory changes will be made to address new challenges and opportunities.
DAS balancing refers to the process of optimizing and adjusting a distributed antenna system (DAS) to ensure that it is providing the best possible signal strength and coverage throughout a building or other structure. The goal is to make sure that the DAS is balanced and the signal is evenly distributed across all areas of the building, with no weak spots or dead zones.
To achieve DAS balancing, the DAS network must be carefully designed and engineered to meet the specific needs of the building or structure. This includes a detailed analysis of the building’s size, layout, and construction materials, as well as the wireless carrier’s coverage requirements and frequency bands.
Once the DAS network is installed, technicians use specialized testing equipment to analyze the signal strength and coverage in different areas of the building. Based on these measurements, they can adjust the DAS settings to ensure that the signal is evenly distributed and optimized for the specific conditions in the building.
DAS balancing is an ongoing process, as changes in the building layout or wireless carrier requirements may require adjustments to the DAS network over time. Regular testing and analysis are essential to ensure that the DAS is providing the best possible coverage and signal strength.
Attenuation refers to the reduction of signal strength as it travels over a transmission medium. In the case of Distributed Antenna Systems (DAS), attenuation can occur as the signal travels over coaxial or fiber optic cables from the headend to the remote antennas.
To mitigate attenuation, DAS designers will often use a combination of amplifiers and equalizers to boost the signal strength and balance it out across the network. Additionally, the use of high-quality cables and connectors can help reduce signal loss due to attenuation.
It’s also important to note that attenuation can vary depending on the frequency of the signal being transmitted. For example, higher frequency signals may experience more attenuation than lower frequency signals, which can impact the design and placement of antennas in the DAS network.
In the context of distributed antenna systems (DAS), there are two main types of systems: passive and active.
A passive DAS relies on a network of passive components, such as splitters, couplers, and combiners, to distribute wireless signals from a source to multiple antennas. Passive DAS systems do not use any active electronic components, such as amplifiers or repeaters, and are often less expensive to install and maintain than active DAS systems. However, they may be less effective in larger or more complex buildings or environments.
An active DAS, on the other hand, uses a network of active electronic components, such as amplifiers and repeaters, to distribute wireless signals from a source to multiple antennas. Active DAS systems can be more effective in larger or more complex buildings or environments, as they can compensate for signal attenuation or interference. However, they can also be more complex and expensive to install and maintain.
The choice between a passive or active DAS system will depend on a number of factors, including the size and complexity of the building or environment, the types of wireless signals being transmitted, and the budget available for installation and maintenance.
Distributed Antenna Systems (DAS) typically consist of the following components:
- Signal source: This is the source of the wireless signal that will be distributed through the DAS. This can include base stations, small cells, or other equipment that connects to the carrier network.
- Donor antenna: This is the external antenna that captures the wireless signal from the signal source.
- Antennas: Antennas are installed throughout the coverage area to ensure that the amplified signal is distributed evenly and effectively. Depending on the specific DAS design, this can include omni-directional antennas, directional antennas, or a combination of both.
- Repeaters: Repeaters are devices that receive and amplify signals from the BDAs and then re-transmit them through the DAS to ensure that the signal strength is maintained across the entire coverage area.
- Distribution cabling: The distribution cabling carries the amplified signal from the repeaters to the antennas that are installed throughout the coverage area. This can include coaxial cable, fiber optic cable, or other types of cabling depending on the specific DAS design.
- Bi-Directional Amplifiers (BDAs): These are the devices that amplify the signal captured by the donor antenna before it is distributed through the DAS. BDAs can be either analog or digital, and can be used to amplify signals for multiple frequency bands.
- Monitoring and control system: This system is used to monitor the performance of the DAS and to ensure that it is operating effectively. It can include a variety of components, such as software, sensors, and other monitoring equipment.

